You can also watch this video
Wireless Communication
Mobile Communication
Mobile Communication Technologies
Network Protocol / Communication Protocol
HTTP
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol)
- TCP: It breaks the data into packets that the network can handle efficiently. It manages the assembling of a message or file into smaller packets that are transmitted over the internet. It verifies all the packets when they arrived at the destination computer and then reassembles them in proper order. Data can be lost in the intermediate network, so TCP adds supports to detect errors or lost data and to Trigger transmission until the data is correctly and completely received.
- IP: The internet protocol (IP) handles the address part of each packet so that it reaches the right destination. It gives a distinct address (called an IP address) to each data packet. It checks this address to see where to forward the message and finally they reassembled at the destination.
PPP (Point to Point Protocol)
PPP is a communication protocol used to establish a direct connection between nodes. It connects nodes without using any device or any host. It is used over phone lines and any other physical cable. It basically designed to help communication between two systems through telephone lines.
Telnet
Telnet is the main protocol for creating a connection with a remote machine. It allows us to connect with a remote computer over a TCP/IP network or internet. Once our Telnet client establishes a connection to the remote host our clients become a virtual terminal, allowing us to communicate with the remote host from our computer with whatever privileges you have been granted to the applications and data on the host computer.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
SMTP is a set of communication protocols that allow the software to transmit an e-mail over the internet. It is a program used for sending emails to other users based on e-mail addresses.
Types of Computer Network
- Personal area network (PAN)
- Local area network (LAN)
- Metropolitan area network (MAN)
- Wide area network (WAN)
Personal area network (PAN)
Local area network (LAN)
Metropolitan area network (MAN)
Wide area network (WAN)
Data Channel
Baud
Bandwidth
Data Transfer Rates
Bit based transfer rates
Byte based transfer rates
Node, Server, and NIC
 |
| Server |
- Dedicated Server
- Non-Dedicated Server
Network Interface Unit (NIU)
- Circuit Switching
- Message Switching
- Packet Switching
1) Circuit Switching
2) Message Switching
3) Packet Switching
Evolution of networking
ARPANET
Internet
Interspace
Introduction of Computer Network.
Network Goals and Applications
- Resource Sharing: The hardware devices like printers and scanners can be shared over a Network. This reduces costs by reducing the number of hardware items.
- Storage Sharing: On a network, the user can access the data of another machine and can store data on another machine.
- Reliability: A file can have copies on two or three different computers. So, if one is not available other copies can be used.
- Access to a remote database: User can access the Host computer at his PC and send the request. For example - users can make flight reservations, book hotels, and so on anywhere in the world with instant confirmation.
- Communication Facilities: Network provides us facilities to communicate with others via Emails, Chats, Video conferencing, and so on.
Disadvantages of Networking
- Complex: Systems are more complex to run.
- Server fails: If all data are held centrally in a server. It may create problems if the central server fails.
- Expensive to install: Cables, Network devices, NIC, and Softwares required for installation of the network. And these are quite expensive.
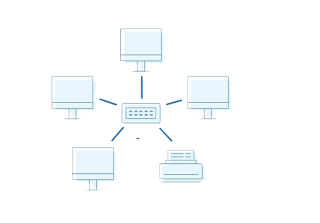
Network Topology
- Bus Topology
- Star Topology
- Mesh Topology
- Ring Topology
- Tree Topology
- Graph Topology
 |
| Bus Topology |
- Reliable, easy to use, and easy to install.
- Additional nodes can easily connect to the existing network at any point.
- Fault detection and isolation is difficult.
- In any case, the failure of the Backbone Network can affect all devices in the network.
- Single connection failure does not affect the entire network.
- Fault detection is easier
- It is easy to add a new node without disturbing the entire network.
- If central Hub fails, the whole network fails.
- Needed a large number of cables so, it increases installation charges.
- Single connection failure does not affect the entire network.
- Fault detection is easier
- Every computer has multiple ways to transfer or receive data.
- Difficult to add a new node.
- Needed a large number of cables so, it increases installation charges.
- Reliable, easy to use, and easy to install.
- Additional nodes can easily connect to the existing network at any point.
- Less expensive
- Fault detection and isolation is difficult.
- The failure of any node of the network can affect all devices in the network.
- Error detection and correction is easy.
- Additional nodes can be added easily.
- When many segments added, Maintenance becomes difficult.
- The failure of the backbone network can affect all devices in the network.