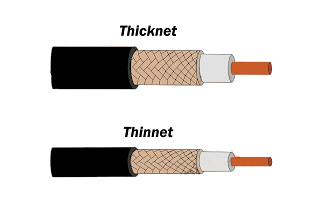
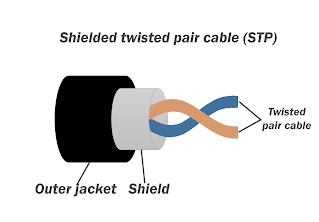
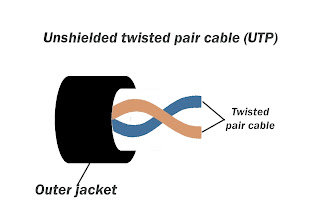
Optical Fiber
- Core - The glass or plastic through which the light travels.
- Cladding - Cover of the core that reflects light back to the core.
- Coating - It protects the fiber cable from a hostile environment.
Types of Optical Fiber Cable
There are two types of Optical Fiber Cable.
- Single-node: It supports a segment length of up to 2 km and bandwidth of up to 100 Mbps.
- Multi-node: It supports a segment length of up to 100 km and bandwidth of up to 2 Gbps.
Advantages of Optical Fiber
- It is immune to electrical and magnetic Interface.
- It is guaranteed secure transmission and has a very high transmission capacity.
- It can be used for broadband.
Disadvantages of Optical Fiber
- It is difficult to install and maintain since they are quite fragile.
- It is most expensive in all the cables.
- Connecting two fiber cable together is a difficult process.